FORMULA
DEGREE OF PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY
DEGREE
|
DESCRIPTION
|
VALUE OF COEFFICIENT
|
SLOPE OF SUPPLY CURVE
|
ELASTIC
|
%CHANGE Qs > %CHANGE P
|
SUPPLY ELASTICITY > 1
|
 |
INELASTIC
|
%CHANGE Qs < %CHANGE P
|
SUPPLY ELASTICITY < 1
|
 |
UNITARY
|
%CHANGE Qs = %CHANGE P
|
SUPPLY ELASTICITY = 1
|
|
PERFECTLY ELASTIC
|
AT LEVEL P,Qs is infinity
|
SUPPLY ELASTICITY = INFINITY
|
|
PERFECTLY INELASTIC
|
NO CHANGE IN Qs ALTHOUGH P CHANGES
|
SUPPLY ELASTICITY = 0
|
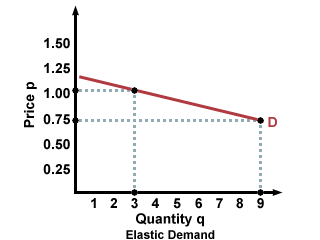
example for Tesco bread
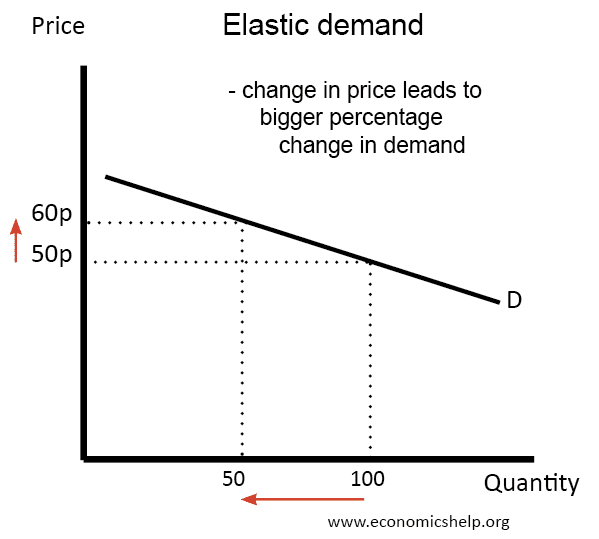
inelastic demand
- for petrol
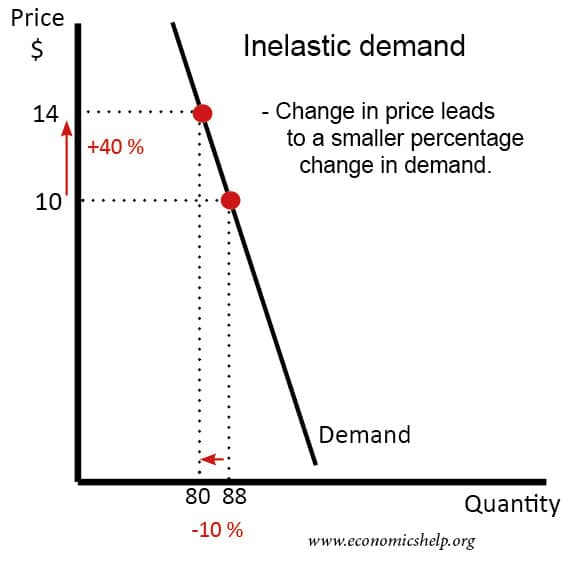
petrol has few alternatives because people with a car need to buy petrol. For many driving is a necessity. There are weak substitutes, such as train, walking and the bus. But, generally, if the price of petrol goes up, demand proves very inelastic.
elasticity of supply

Given the following data for the supply and demand of movie tickets, calculate the price elasticity of supply when the price changes from $9.00 to $10.00.

We know that the original price is $9 and the new price is $10, so we have Price (Old) =$9 and Price (New) = $10. From the chart, we see that the quantity supplied when the price is $9 is 75 and when the price is $10 is 105.
So we have:
Price (Old) = $9
Price (New) = $10
Price (New) = $10
Quantity Supplied (Old) = 75
Quantity Supplied (New) = 105


No comments:
Post a Comment